FastAPI로 완벽한 블로그 만들기: 댓글 시스템
Grace Collins
Solutions Engineer · Leapcell

이전 글에서 FastAPI 블로그에 대한 사용자 로그인 및 세션 관리를 완벽하게 구현했습니다. 이제 서버는 사용자의 로그인 상태를 "기억"하고 인증이 필요한 페이지를 보호할 수 있습니다.
이제 로그인한 사용자와 게스트를 구별할 수 있으므로 블로그에 대화형 기능을 추가하기에 완벽한 시점입니다.
이 글에서는 블로그에 기본적이면서도 중요한 기능인 댓글 시스템을 추가해 보겠습니다.
구체적으로 다음 기능들을 구현할 것입니다.
- 각 게시물 아래에 댓글 목록 표시.
- 로그인한 사용자가 게시물에 댓글을 작성할 수 있도록 허용.
1단계: 댓글에 대한 데이터 모델 생성
Post 및 User 모델과 마찬가지로 Comment 모델도 자체 데이터 모델과 Post 및 User와의 관계가 필요합니다.
1.1. Comment 모델 생성
models.py 파일을 열고 Comment 모델을 추가한 다음 User 및 Post 모델을 업데이트하여 양방향 관계를 설정합니다.
# models.py import uuid from datetime import datetime from typing import Optional, List from sqlmodel import Field, SQLModel, Relationship class User(SQLModel, table=True): id: Optional[uuid.UUID] = Field(default_factory=uuid.uuid4, primary_key=True) username: str = Field(unique=True, index=True) password: str # Comment와의 일대다 관계 추가 comments: List["Comment"] = Relationship(back_populates="user") class Post(SQLModel, table=True): id: Optional[uuid.UUID] = Field(default_factory=uuid.uuid4, primary_key=True) title: str content: str createdAt: datetime = Field(default_factory=datetime.utcnow, nullable=False) # Comment와의 일대다 관계 추가 comments: List["Comment"] = Relationship(back_populates="post") class Comment(SQLModel, table=True): id: Optional[uuid.UUID] = Field(default_factory=uuid.uuid4, primary_key=True) content: str createdAt: datetime = Field(default_factory=datetime.utcnow, nullable=False) # Post 및 User 테이블을 연결하는 외래 키 정의 postId: uuid.UUID = Field(foreign_key="post.id") userId: uuid.UUID = Field(foreign_key="user.id") # 다대일 관계 정의 post: Post = Relationship(back_populates="comments") user: User = Relationship(back_populates="comments")
여기서 세 가지를 수행했습니다.
content,createdAt, 그리고post및user테이블을 가리키는 외래 키postId및userId를 포함하는Comment모델을 생성했습니다.Comment모델에서Relationship을 사용하여Post및User와의 "다대일" 관계를 정의했습니다.User및Post모델에 역방향 "일대다" 관계인comments를 추가했습니다. 이를 통해Post객체 또는User객체의 모든 댓글을 쉽게 검색할 수 있습니다.
main.py에서 create_db_and_tables 함수를 구성했기 때문에 애플리케이션이 시작될 때 SQLModel 모델을 자동으로 감지하고 해당 데이터베이스 테이블을 생성하거나 업데이트합니다. SQL을 수동으로 실행할 필요가 없습니다.
수동으로 SQL을 실행해야 하고 Leapcell 에서 데이터베이스를 생성한 경우,
웹사이트의 데이터베이스 관리 페이지로 이동하여 위의 문장을 SQL 인터페이스에 붙여넣고 실행하기만 하면 됩니다.
2단계: 댓글에 대한 비즈니스 로직 구현
다음으로 댓글 생성 및 쿼리를 처리하는 함수를 만듭니다.
프로젝트의 루트 디렉터리에 comments_service.py라는 새 파일을 만들어 댓글 관련 비즈니스 로직을 저장합니다.
# comments_service.py import uuid from typing import List from sqlmodel import Session, select from models import Comment def get_comments_by_post_id(post_id: uuid.UUID, session: Session) -> List[Comment]: """주어진 게시물 ID에 대한 모든 댓글을 찾아 생성 시간을 기준으로 오름차순으로 정렬합니다.""" statement = select(Comment).where(Comment.postId == post_id).order_by(Comment.createdAt) comments = session.exec(statement).all() return comments def create_comment(content: str, user_id: uuid.UUID, post_id: uuid.UUID, session: Session) -> Comment: """새 댓글을 생성합니다.""" new_comment = Comment(content=content, userId=user_id, postId=post_id) session.add(new_comment) session.commit() session.refresh(new_comment) return new_comment
get_comments_by_post_id 함수는 게시물 아래의 모든 댓글을 가져오는 데 사용됩니다. create_comment 함수는 새 댓글을 데이터베이스에 저장하는 데 사용됩니다. 모델에서 Relationship을 올바르게 설정했기 때문에 나중에 템플릿에서 comment.user.username을 통해 작성자의 사용자 이름을 편리하게 액세스할 수 있습니다.
3단계: 댓글 제출 및 표시를 위한 라우트 생성
이제 댓글 기능을 게시물 페이지에 통합해야 합니다. 여기에는 사용자 제출 댓글을 처리하는 백엔드 라우트와 댓글을 표시하기 위해 게시물 상세 페이지 라우트를 업데이트하는 두 가지 부분이 필요합니다.
3.1. 댓글 라우트 생성
routers 폴더에 comments.py라는 새 파일을 만듭니다.
# routers/comments.py import uuid from fastapi import APIRouter, Depends, Form from fastapi.responses import RedirectResponse from sqlmodel import Session from database import get_session import comments_service from auth_dependencies import login_required router = APIRouter() @router.post("/posts/{post_id}/comments") def create_comment_for_post( post_id: uuid.UUID, content: str = Form(...), user: dict = Depends(login_required), # 사용자가 로그인했는지 확인하기 위한 의존성 주입 session: Session = Depends(get_session) ): # 세션의 사용자 ID는 문자열이므로 UUID 유형으로 변환해야 합니다. user_id = uuid.UUID(user["id"]) comments_service.create_comment( content=content, user_id=user_id, post_id=post_id, session=session ) # 성공적인 댓글 작성 후 게시물 페이지로 다시 리디렉션 return RedirectResponse(url=f"/posts/{post_id}", status_code=302)
이 라우트는 POST 요청만 처리합니다. 이전에 만든 login_required 의존성을 사용하여 보호하므로 로그인한 사용자만 댓글을 작성할 수 있습니다. 댓글이 성공적으로 생성되면 페이지가 원래 게시물 상세 페이지로 다시 리디렉션됩니다.
3.2. 메인 애플리케이션 및 게시물 라우트 업데이트
먼저 main.py에서 방금 생성한 댓글 라우터를 마운트합니다.
# main.py # ... 다른 임포트 ... from routers import posts, users, auth, comments # comments 라우터 임포트 # ... app = FastAPI(lifespan=lifespan) # ... # 라우터 포함 app.include_router(posts.router) app.include_router(users.router) app.include_router(auth.router) app.include_router(comments.router) # comments 라우터 마운트
다음으로 routers/posts.py의 get_post_by_id 함수를 수정하여 해당 게시물에 대한 모든 댓글을 가져와 템플릿에 전달하도록 합니다.
# routers/posts.py # ... 임포트 ... from auth_dependencies import get_user_from_session import comments_service # comment 서비스 임포트 # ... 라우터 및 템플릿 정의 ... # ... 다른 라우트 ... @router.get("/posts/{post_id}", response_class=HTMLResponse) def get_post_by_id( request: Request, post_id: uuid.UUID, session: Session = Depends(get_session), user: dict | None = Depends(get_user_from_session) ): post = session.get(Post, post_id) # 이 게시물에 대한 모든 댓글 가져오기 comments = comments_service.get_comments_by_post_id(post_id, session) # 게시물, 사용자 및 댓글을 함께 템플릿에 전달 return templates.TemplateResponse( "post.html", { "request": request, "post": post, "title": post.title, "user": user, "comments": comments # 새로 추가 } )
4단계: 프론트엔드 뷰 업데이트
마지막 단계는 템플릿 파일을 수정하여 댓글 목록과 댓글 폼을 표시하는 것입니다.
templates/post.html을 열고 게시물 내용과 뒤로 가기 링크 사이에 다음 코드를 추가합니다.
<div class="post-content">{{ post.content | replace('\n', '<br>') | safe }}</div> </article> <section class="comments-section"> <h3>Comments</h3> <div class="comment-list"> {% if comments %} {% for comment in comments %} <div class="comment-item"> <p class="comment-content">{{ comment.content }}</p> <small> By <strong>{{ comment.user.username }}</strong> on {{ comment.createdAt.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') }} </small> </div> {% endfor %} {% else %} <p>No comments yet. Be the first to comment!</p> {% endif %} </div> {% if user %} <form action="/posts/{{ post.id }}/comments" method="POST" class="comment-form"> <h4>Leave a Comment</h4> <div class="form-group"> <textarea name="content" rows="4" placeholder="Write your comment here..." required></textarea> </div> <button type="submit">Submit Comment</button> </form> {% else %} <p><a href="/auth/login">Login</a> to leave a comment.</p> {% endif %} </section> <a href="/" class="back-link">← Back to Home</a> {% include "_footer.html" %}
{% for comment in comments %}를 사용하여 모든 댓글을 반복하고 표시합니다.comment.user.username을 통해 작성자 이름을 직접 표시할 수 있습니다.{% if user %}를 사용하여 사용자가 로그인했는지 확인합니다. 로그인한 경우 댓글 폼이 표시되고, 그렇지 않으면 로그인 링크가 표시됩니다.
페이지를 더 보기 좋게 만들려면 public/css/style.css에 스타일을 추가할 수 있습니다.
/* ... 다른 스타일 ... */ .comments-section { margin-top: 3rem; border-top: 1px solid #eee; padding-top: 2rem; } .comment-list .comment-item { background: #f9f9f9; border: 1px solid #ddd; padding: 1rem; border-radius: 5px; margin-bottom: 1rem; } .comment-content { margin-top: 0; } .comment-item small { color: #666; } .comment-form { margin-top: 2rem; } .comment-form textarea { width: 100%; padding: 0.5rem; margin-bottom: 1rem; border: 1px solid #ccc; border-radius: 4px; }
실행 및 테스트
이제 애플리케이션을 다시 시작합니다.
uvicorn main:app --reload
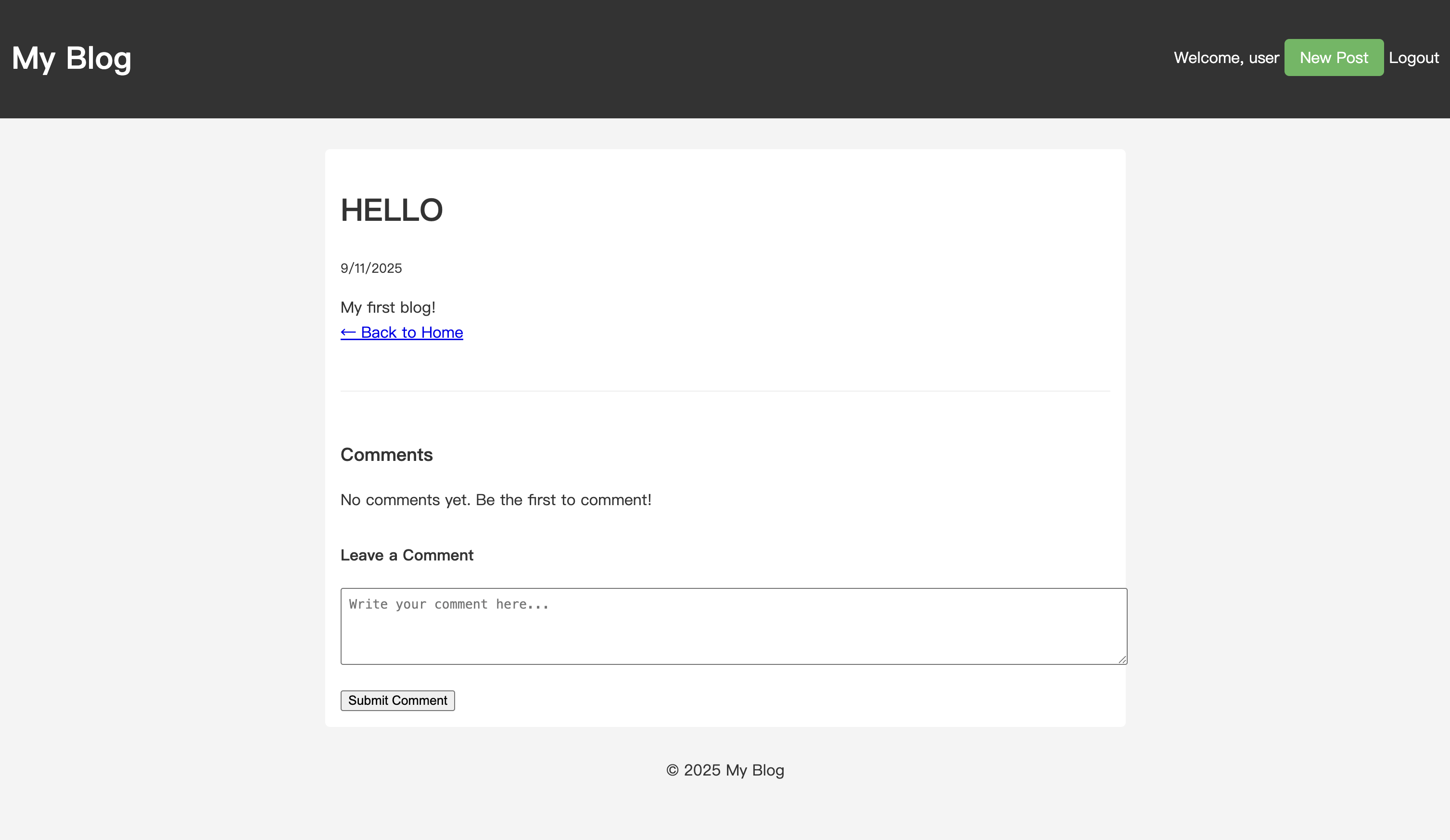
브라우저를 열고 게시물의 상세 페이지로 이동합니다. 새 댓글 섹션이 표시됩니다.
댓글 상자에 내용을 입력하고 제출합니다. 페이지가 새로고침된 후 댓글 목록에서 방금 게시한 댓글을 볼 수 있습니다.
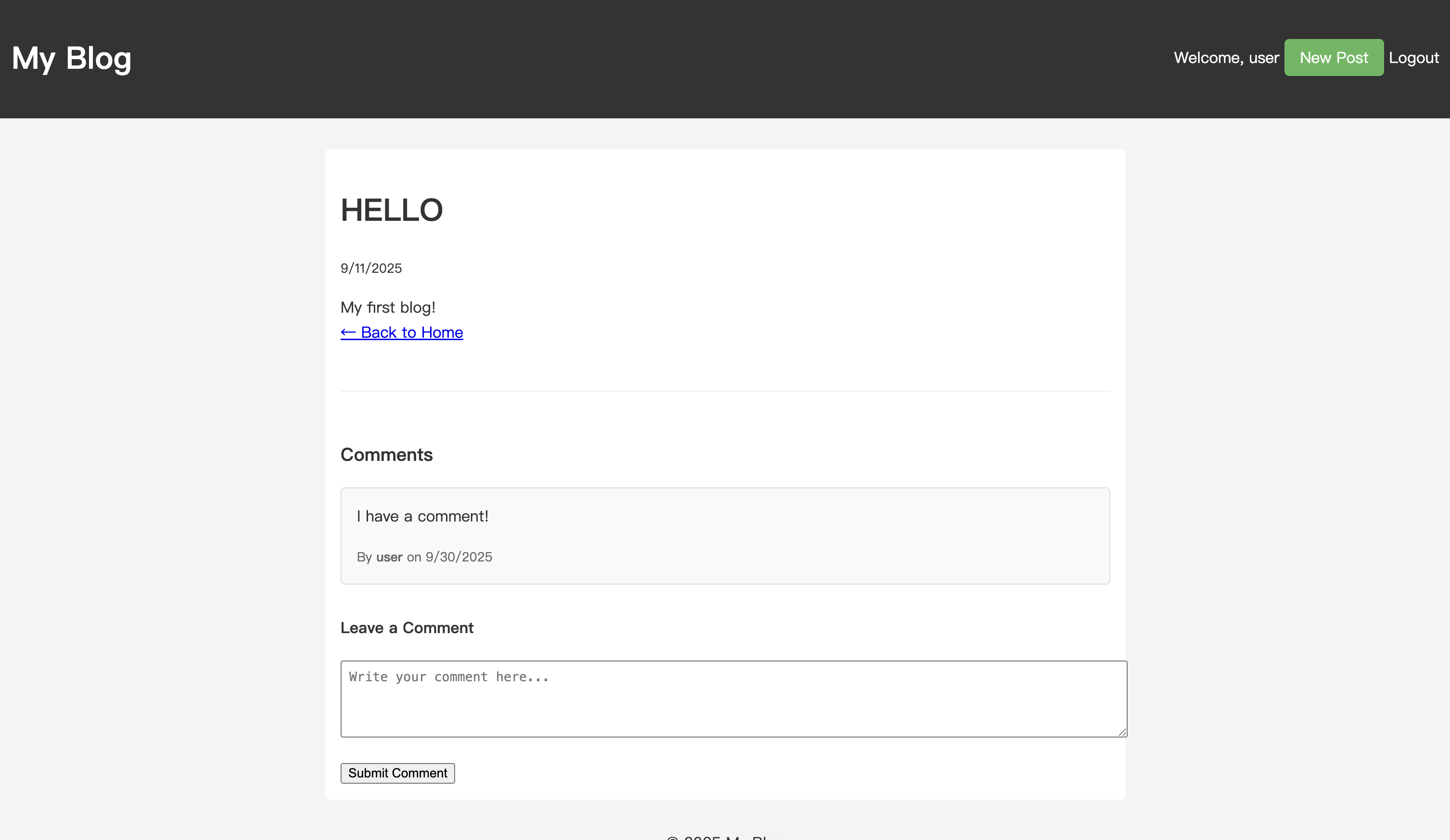
블로그에 댓글 시스템을 성공적으로 추가했습니다!
물론 현재 댓글 기능은 여전히 매우 기본적인 상태입니다. 다음 글에서는 작성자가 댓글에 답글을 작성하는 로직을 구현하여 블로그의 상호 작용성을 한 단계 더 끌어올리면서 이 기능을 계속 향상시킬 것입니다.



